The consumption of renewable sources of energy will always be in demand due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Among the various photovoltaic solutions available today, thin-film solar panels are a competing and highly chosen alternative. Most importantly, its lightweight nature, flexibility, and ease of integration make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential requirements to large-scale industrial deployments to mobile power solutions. This article will provide you with the details on how thin-film solar panels work, their advantages and limitations, and where they stand in the evolving solar energy market.
What Are Thin-Film Solar Panels?
Thin-film solar panels are a type of photovoltaic (PV) technology made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate, such as glass, plastic, or metal. These layers are significantly thinner than those found in conventional silicon solar panels, often just a few micrometers thick. As a result, these solar panels are lightweight, flexible, and easier to manufacture in a variety of sizes and shapes.
The three most common types of thin-film technologies are:
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe): The most widely used thin-film technology, CdTe panels are known for their relatively low production cost and good performance in low-light and high-temperature conditions.
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si): This type uses non-crystalline silicon and offers a lower efficiency rate but is more eco-friendly and flexible than crystalline silicon.
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS): CIGS panels have higher efficiency compared to other thin-film types and can be deposited on flexible substrates, making them ideal for unique applications.
How Do They Work?
Like traditional solar panels, thin-film solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. However, due to their distinct manufacturing process, they behave somewhat differently under real-world conditions.
Instead of slicing silicon wafers, manufacturers deposit semiconductor materials in thin layers onto a backing surface. This approach requires less raw material and energy to produce, lowering the overall environmental impact of manufacturing.
The flexibility of thin-film solar cells means they can be used in innovative applications, such as on curved surfaces, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), or even on consumer electronics and vehicles.
Advantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
The solar panels come with a host of benefits that set them apart from traditional silicon-based PV systems.
1. Lightweight and Flexible
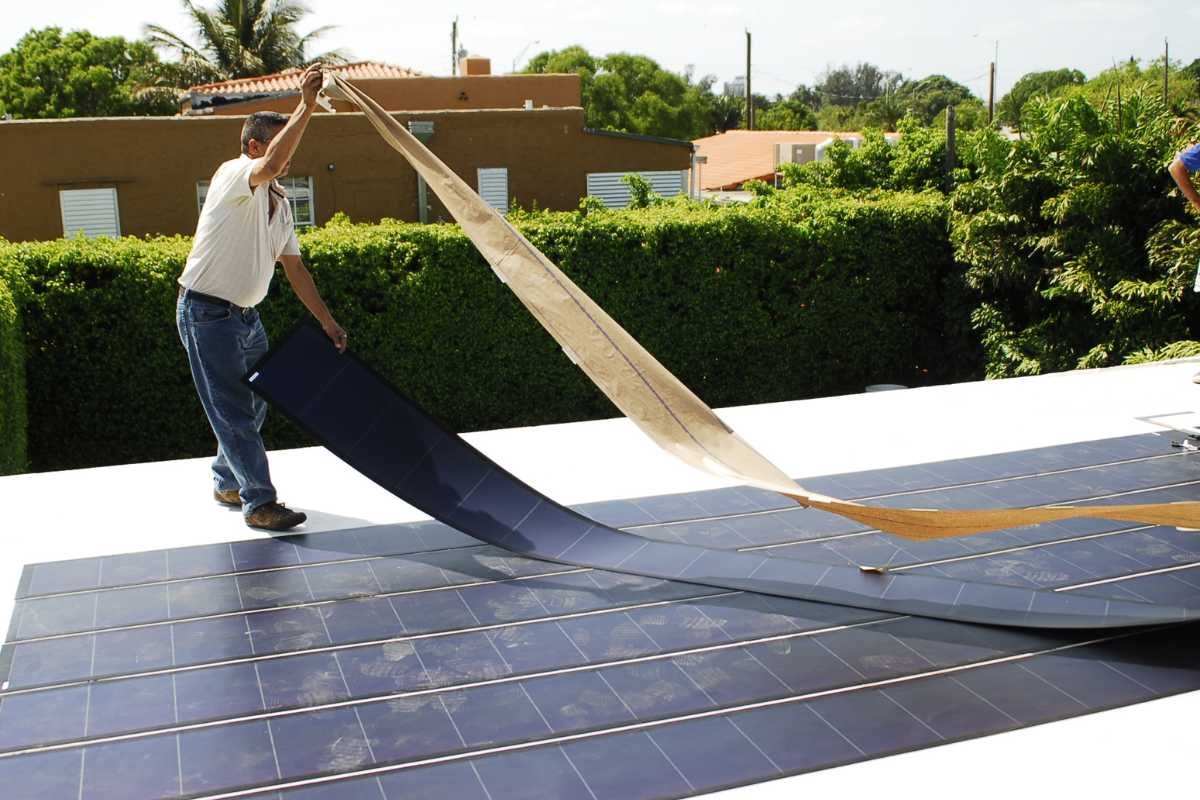

One of the most attractive features of thin-film solar panels is their low weight. Because they don’t rely on thick glass or heavy silicon wafers, they can be installed on surfaces that cannot bear the weight of conventional panels. This includes rooftops with structural limitations, portable systems, and off-grid setups like RVs or boats.
2. Better Performance in Low-Light and High-Temperature Conditions
Unlike crystalline silicon panels, which can lose efficiency at high temperatures, thin-film solar panels maintain performance more effectively. They are also less sensitive to partial shading and low-light conditions, making them suitable for regions with variable weather or less-than-ideal installation angles.
3. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Since thin-film panels require less material and energy during production, their initial manufacturing costs are typically lower than those of traditional panels. This makes them attractive for large-scale solar farms, especially where space and weight are not major concerns.
4. Aesthetics and Versatility
The sleek, uniform look of thin-film panels is often considered more visually appealing than the grid-like appearance of silicon panels. Additionally, because they can be made flexible, they are ideal for building-integrated applications such as solar windows, facades, and even solar roof tiles.
Limitations of Thin-Film Solar Panels
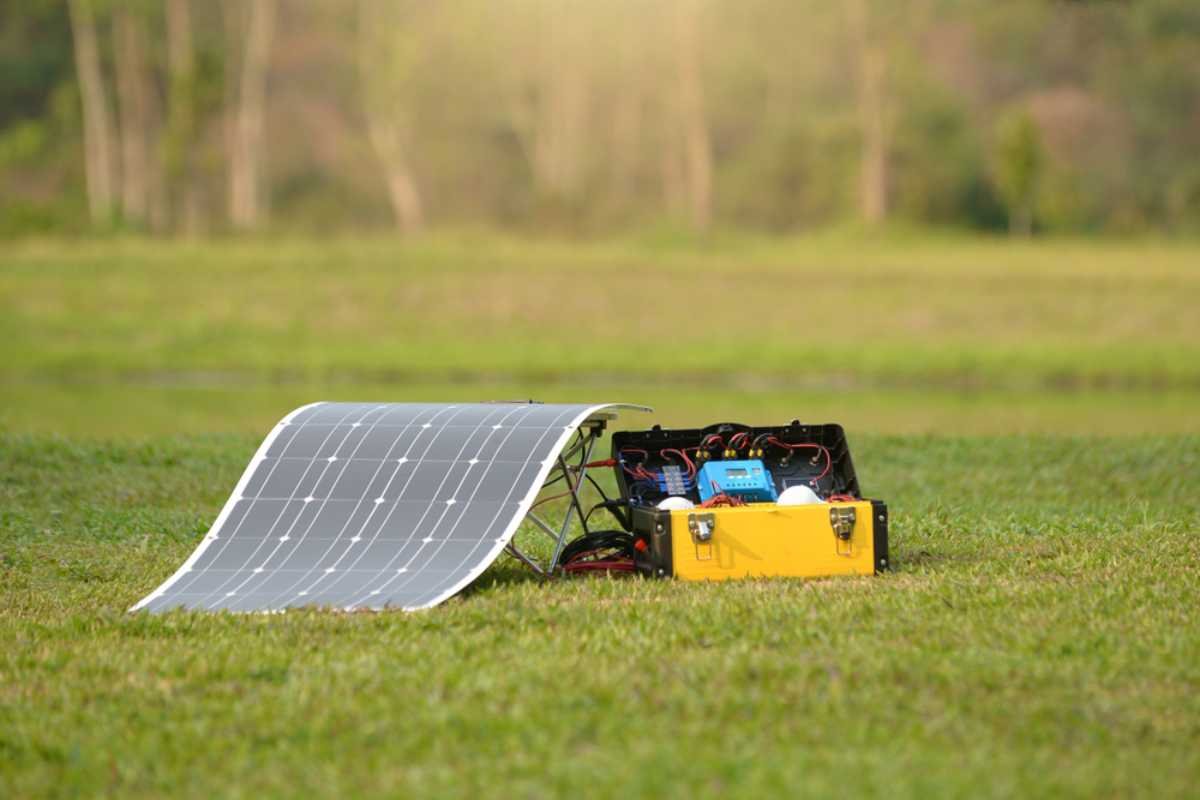

Despite their many advantages, thin-film solar panels come with some trade-offs that limit their widespread adoption.
1. Lower Efficiency
Thin-film technologies generally have lower efficiency rates than crystalline silicon panels. While traditional panels can exceed 20% efficiency, most thin-film options fall between 10% and 15%. This means more surface area is required to generate the same amount of electricity, a significant factor in space-constrained installations.
2. Shorter Lifespan and Warranty
Although improvements are ongoing, thin-film panels tend to have shorter operational lifespans and lower warranties compared to traditional panels. Most come with warranties of around 10–20 years, whereas crystalline panels often have 25–30-year warranties.
3. Environmental Concerns
Some thin-film technologies use materials that are less environmentally friendly or harder to recycle. For example, CdTe contains cadmium, a toxic heavy metal, which raises concerns about its disposal and environmental impact at the end of its life cycle.
Applications of Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thanks to their unique properties, thin-film solar panels are being used in a variety of innovative applications that go beyond traditional rooftop installations.
1. Commercial and Industrial Rooftops
In cases where buildings cannot support heavy loads, it offers a viable alternative. Their lightweight design makes them ideal for commercial rooftops with structural limitations.
2. Portable and Off-Grid Systems
For campers, military use, and emergency response, portable thin-film solar panels offer a reliable and lightweight solution to generate electricity on the move. Their flexibility and durability are key assets in such environments.
3. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Thin-film technologies are increasingly being integrated into building materials, such as solar shingles, glass facades, and windows, allowing architects to design energy-efficient buildings without compromising aesthetics.
4. Transportation and Consumer Products
Some electric vehicles and consumer gadgets now incorporate thin-film solar cells to supplement power needs. From solar-powered backpacks to car roofs that extend battery range, the possibilities are expanding rapidly.
Market Outlook and Trends
As of 2025, the global solar market is still dominated by crystalline silicon technologies, but thin-film solar panels are carving out a niche in specific applications. Their use is expected to grow in sectors that demand lightweight, flexible, or integrated energy solutions.
Several research efforts are underway to improve the efficiency, durability, and sustainability of thin-film technologies. Notably, hybrid systems combining thin-film with other energy sources or storage systems are gaining attention for enhancing overall efficiency.
Moreover, innovations in roll-to-roll manufacturing and printing techniques are expected to reduce production costs even further, potentially making thin-film solar panels more competitive with their crystalline counterparts shortly.
Conclusion
Thin-film solar panels provide a unique approach to capturing solar energy. It gives benefits where traditional panels fail, such as lightweight structure, adaptability, and aesthetic appeal. Some cons, like not matching the efficiency and longevity of crystalline silicon, can be overshadowed by the pros, like BIPV, portable systems, and weight-sensitive installations. This form of solar panel will establish a crucial place in the future of renewable energy. The thin-film solar panels continue to grow with every evolution of solar technology. This solar panel is a must-choose option who want to have a beyond conventional, more adaptable, and design-friendly solar future.













